Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal? 3 Powerful Tactics to Spread its Message
Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal? PETA’s anti-fur campaign is one of the organization’s most recognizable and divisive initiatives. Known for its striking visuals, celebrity endorsements, and unyielding stance on animal rights, the campaign has worked tirelessly to raise awareness about the ethical implications of wearing fur. While the campaign has achieved success in many parts of the world, it has faced resistance and criticism in others.
This article seeks to analyze whether PETA’s anti-fur campaign has been universally embraced or if its impact has been more localized.

Table of Contents
- What is the Anti-Fur Campaign?
- What is PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign? Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
- Global Reception of PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
- Also Read About How Does Pet Grooming Relate to Agriculture?
- Cultural Significance of Fur in Different Regions
- Impact on the Fashion Industry: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
- Economic Impacts on Fur Industry Workers: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
- Celebrity Endorsement and Media Influence
- Legislative and Policy Changes Due to PETA’s Campaign
- PETA’s Influence on Alternative Materials in Fashion
- Challenges and Controversies Surrounding the Campaign
- Public Opinion and Support for Anti-Fur Campaigns
- PETA’s Legacy and Long-Term Impact
- Conclusion
- FAQs: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal?
What is the Anti-Fur Campaign?
Results: The anti-fur campaign has led numerous luxury brands, including Gucci, Versace, Prada, and others, to stop using fur in their collections. Public opinion on fur has also shifted, with more people opting for faux fur or other alternatives due to the campaign’s impact.

Overview: PETA’s anti-fur campaign is a high-profile initiative aimed at ending the use of animal fur in fashion. The campaign uses public demonstrations, celebrity endorsements, and educational resources to highlight the cruelty of fur farming, where animals are often kept in cramped cages and killed in painful ways.
What is PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign? Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
Launched in the 1980s, PETA’s anti-fur campaign sought to address the inhumane practices involved in the fur industry. The organization’s messaging centered on the cruelty of fur farming, where animals such as minks, foxes, and rabbits are bred and killed for their fur in often brutal conditions. The campaign’s main goal was to make people aware of the suffering that these animals endure for fashion, hoping to influence consumer purchasing decisions.
PETA employed various tactics to spread its message, here are 3 powerful tactics to spread its message:
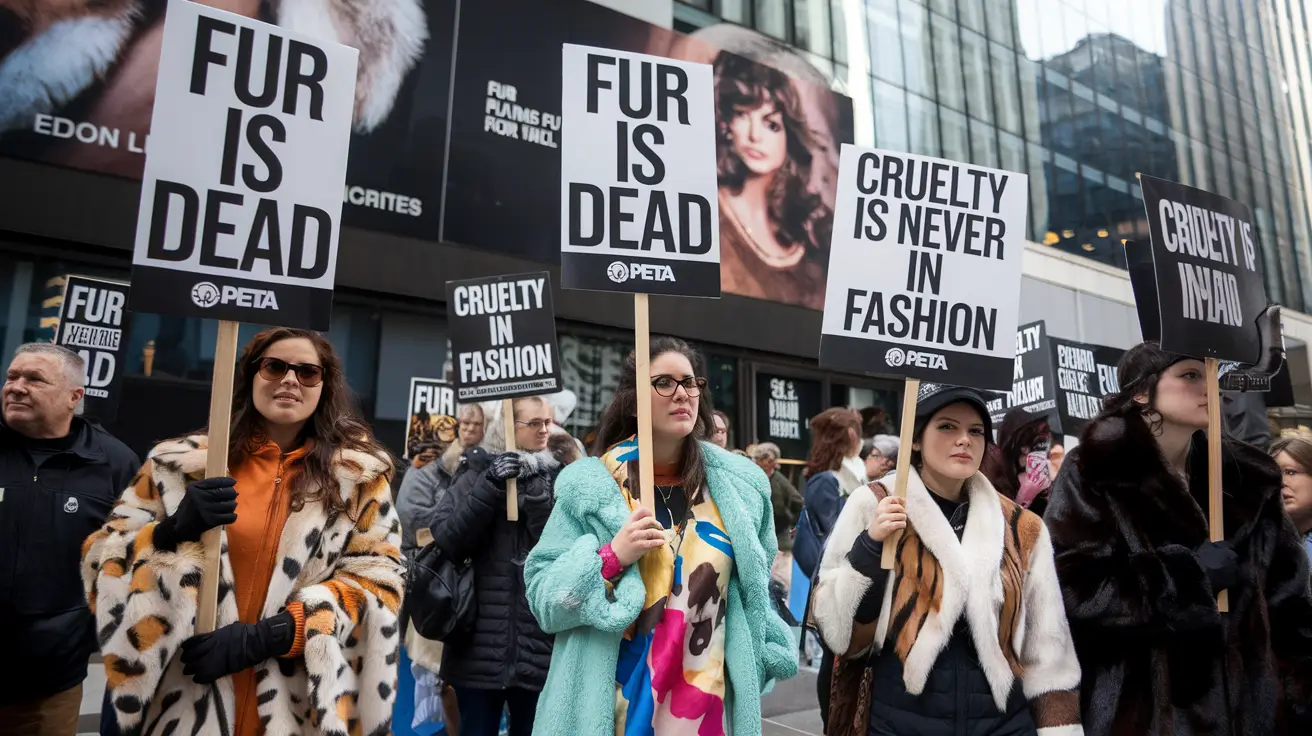
- Iconic Advertisements: Perhaps the most famous is PETA’s “I’d Rather Go Naked Than Wear Fur” campaign, which featured high-profile celebrities posing without fur clothing.
- Protests and Demonstrations: PETA frequently held eye-catching protests outside fur stores, designer boutiques, and fashion events, garnering attention through shock tactics.
- Celebrity Involvement: PETA enlisted a range of celebrities to support its cause, including the likes of Pamela Anderson, Khloe Kardashian, and Ellen DeGeneres. Celebrity endorsements played a crucial role in giving the campaign visibility and lending it credibility.
These efforts were designed to make fur an unpopular choice by associating it with cruelty and inhumanity.
Global Reception of PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
While PETA’s anti-fur campaign gained significant traction in many Western countries, its reception was not universal. The campaign found particular success in urban centers where there was a strong focus on ethical fashion, sustainability, and animal rights.
Cities like New York, Los Angeles, and London saw major shifts in consumer behavior as people began to question the ethics of wearing fur. Additionally, countries like the UK and the US saw policy changes, with some fur farming bans and a decrease in fur sales.

However, the campaign struggled to make similar inroads in regions with deeply ingrained fur traditions. In places like Russia, Canada, and Scandinavia, fur is not only seen as a fashion statement but also a necessity in colder climates.
The cultural and economic ties to fur were strong, making the anti-fur message less effective in those regions. Fur was, and in some cases still is, seen as a part of national heritage, and PETA’s campaign was sometimes viewed as an attack on these traditions.
Also Read About How Does Pet Grooming Relate to Agriculture?
Cultural Significance of Fur in Different Regions
Fur has held various cultural significance throughout history. In colder regions like northern Europe, Canada, and Russia, fur was not just a fashion choice but a vital part of survival. For indigenous groups and rural communities, fur was essential for warmth and protection against the elements, making it difficult for PETA’s message to resonate in these areas.
In contrast, in urban settings where animal rights movements gained more ground, fur became more associated with luxury and status. The rise of “fast fashion” in Western countries led to an increasing demand for synthetic alternatives, but the luxury fur market persisted. The cultural divide between utilitarian fur use and fur as a fashion statement made PETA’s message challenging to implement universally.
Impact on the Fashion Industry: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
PETA’s campaign had a transformative effect on the fashion industry, particularly in Western markets. The organization’s efforts helped to shift attitudes toward fur, making it less socially acceptable to wear animal fur.
Several high-profile fashion houses, including Gucci, Prada, and Versace, eventually adopted fur-free policies. This was a direct response to changing consumer preferences and the mounting pressure from activists and animal rights organizations.
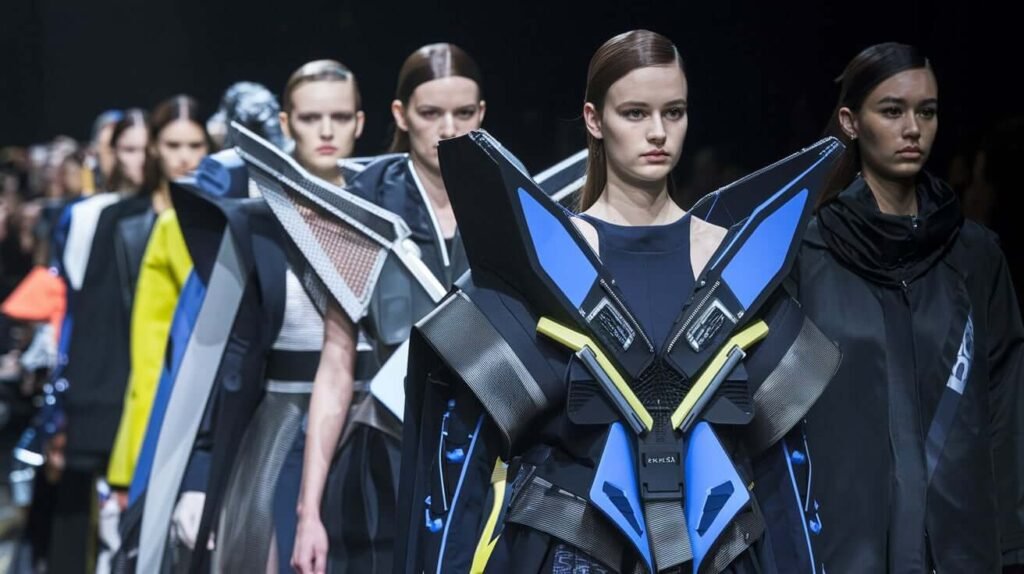

However, the fur industry still maintains a presence in global fashion, particularly in luxury markets. While some brands have made the transition to cruelty-free alternatives like faux fur, others continue to feature fur in their collections. This has resulted in an ongoing debate about whether the fur industry will eventually fade into obscurity or whether it will continue to thrive in niche markets.
Economic Impacts on Fur Industry Workers: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal
The fur industry is a major source of employment in some parts of the world. For example, in countries like Denmark, Finland, and China, fur farming has been a significant economic contributor.
PETA’s anti-fur campaign, while effective in reducing consumer demand, has been met with resistance in regions where the fur trade is economically vital. Workers in the fur industry have voiced concerns about losing their jobs and livelihood as consumer demand for fur declines.
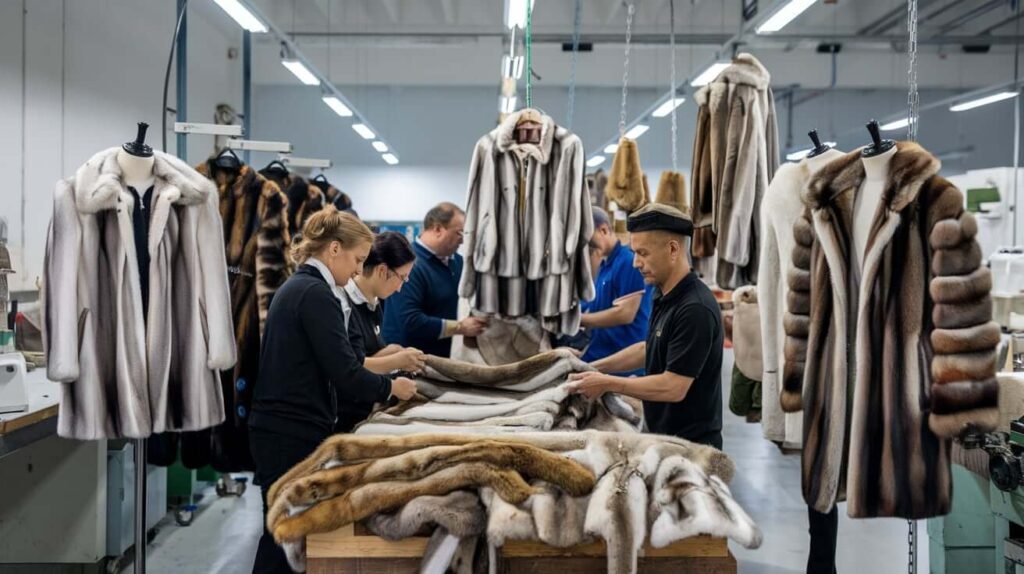

In response to this, some regions have implemented compensation or retraining programs to help workers transition to other industries. Nevertheless, the economic impact on these communities remains a contentious issue.
Celebrity Endorsement and Media Influence
One of the most effective aspects of PETA’s anti-fur campaign was its ability to harness the power of celebrity endorsements. High-profile figures like Pamela Anderson and Charlize Theron, who participated in PETA’s “I’d Rather Go Naked Than Wear Fur” campaign, brought attention to the cause. Their involvement helped to spark a broader discussion about animal rights and ethical fashion.

While celebrity support undoubtedly increased awareness, it also drew criticism. Some questioned the sincerity of these endorsements, pointing out that some of these celebrities wore fur in their private lives despite their public advocacy. This inconsistency led to skepticism about the true motivations behind the campaign.
Legislative and Policy Changes Due to PETA’s Campaign
In addition to influencing fashion, PETA’s anti-fur campaign also impacted legislation. In several countries, PETA’s lobbying efforts have contributed to fur farming bans, such as those in the UK and the Netherlands. The organization also pushed for bans on fur sales in various cities and regions, such as in Los Angeles and San Francisco, where fur sales are now banned.
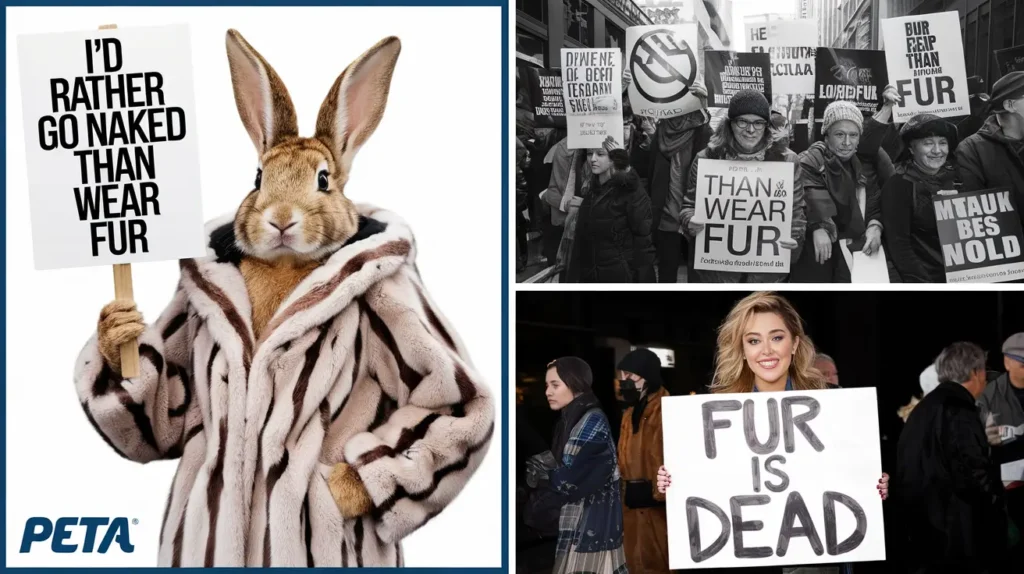

These legislative changes indicate a shift in public opinion and a growing recognition of animal welfare concerns. PETA’s campaign was instrumental in generating the public discourse that led to these legal reforms, positioning animal rights as a key factor in policy decisions.
PETA’s Influence on Alternative Materials in Fashion
Another significant impact of PETA’s anti-fur campaign is the rise of ethical and sustainable alternatives to fur. As the demand for cruelty-free fashion increased, brands and designers turned to innovative materials that mimic the look and feel of real fur without the ethical concerns.
Faux fur, for example, became a widely accepted substitute in the fashion industry, and its popularity continues to grow.
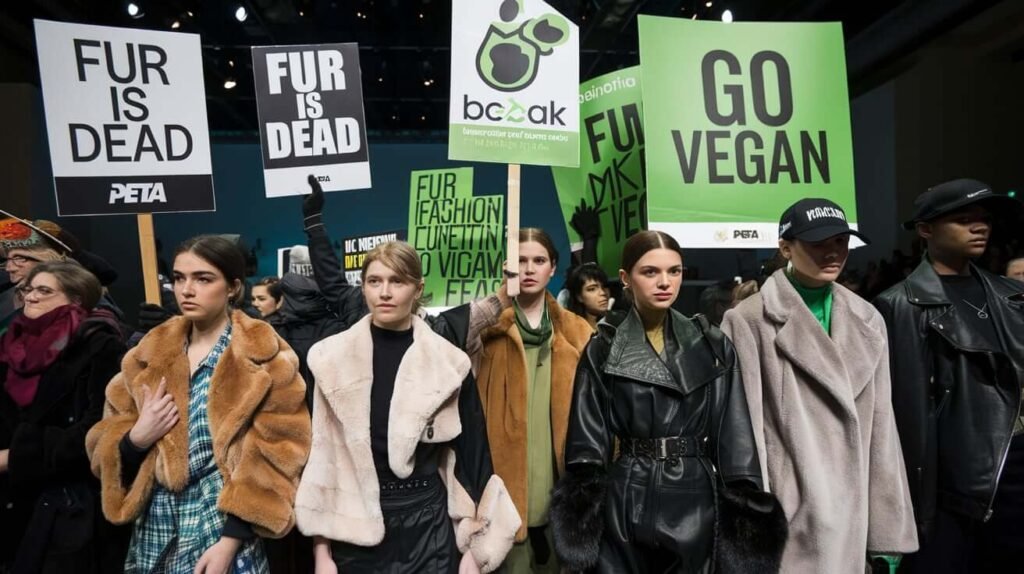

Additionally, many brands that once used real fur now tout their commitment to cruelty-free fashion by offering faux fur, vegan leather, and other sustainable alternatives. These materials, along with a growing focus on sustainable fashion practices, reflect a broader movement within the fashion industry that was partly influenced by PETA’s anti-fur campaign. The success of these alternatives helped reduce the demand for real fur, particularly in high fashion and luxury markets.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding the Campaign
Despite its successes, PETA’s anti-fur campaign has faced several challenges and controversies. One major criticism is PETA’s aggressive tactics, which some view as too confrontational and alienating.
The organization’s shock-value ads, protests, and public demonstrations sometimes caused backlash, with critics accusing PETA of being too radical or dismissive of cultural and economic contexts where fur is still important.

Another point of contention has been the organization’s treatment of the animals in its own campaigns. While PETA champions animal rights, its use of controversial methods has drawn criticism from within the animal rights community itself. Some believe that PETA’s sometimes sensationalist approach undermines its message and alienates potential supporters who might otherwise be sympathetic to the cause.
Furthermore, the use of celebrity endorsements has not been without controversy. Celebrities, often the face of PETA’s campaigns, have sometimes been accused of hypocrisy for wearing fur or leather products outside of their public campaigns. This inconsistency has, at times, diminished the effectiveness of their messaging.
Public Opinion and Support for Anti-Fur Campaigns
Public opinion about fur has undergone a substantial shift over the past few decades. PETA’s anti-fur campaign has played a crucial role in shifting consumer attitudes, particularly in Western countries where fur was once a symbol of wealth and status.
Surveys have shown a growing awareness of animal cruelty associated with fur production, with more people opting for cruelty-free fashion options.

However, the campaign’s success has been uneven. While many consumers are now more conscious of the ethical implications of their purchases, there are still sizable groups that support the fur industry. For some, wearing fur remains a fashion choice or cultural tradition, while others simply prioritize affordability over ethical considerations.
PETA’s Legacy and Long-Term Impact
PETA’s anti-fur campaign has left a lasting legacy, not just in terms of public awareness of animal cruelty but also in the broader movement toward ethical fashion. While fur is no longer as fashionable as it once was, PETA’s efforts have contributed to the shift toward vegan leather, faux fur, and sustainable materials, encouraging a more eco-conscious and animal-friendly approach to fashion.
This legacy extends beyond fur and has set the stage for other animal rights campaigns, influencing how consumers view the ethical dimensions of their purchases.
The long-term impact of PETA’s anti-fur campaign is evident in the decline of the global fur market and the rise of alternative materials. PETA has succeeded in making fur a contentious issue in the world of fashion, prompting brands to reconsider their use of animal products.
Has PETA Accomplished Anything?
- Policy Changes: PETA has influenced companies, government policies, and institutions to adopt cruelty-free practices. For instance, PETA’s campaigns have led to the end of animal testing by some large corporations and influenced cosmetics companies to go cruelty-free.
- Public Awareness: Through public campaigns, PETA has brought significant attention to issues like factory farming, animal testing, fur farming, and more, shaping public opinion and awareness about animal rights.
- Influence on Industries: PETA has made strides in changing the practices of fashion, food, and entertainment industries. Many fashion brands now avoid animal-derived materials like fur and exotic skins, and some fast-food chains offer plant-based options due to consumer pressure inspired by PETA’s advocacy.
How Has PETA Changed the World?
- Animal Testing: PETA’s work has led to bans on animal testing for cosmetics in several regions, including the European Union. They have raised awareness about alternatives, such as in-vitro testing and computer modeling, and successfully convinced companies to adopt these practices.

- Public Awareness and Education: PETA has educated millions of people worldwide about animal rights issues, including veganism, animal cruelty, and factory farming. This has led to a notable rise in vegan and cruelty-free lifestyle choices.
- Legal and Industry Changes: PETA has pushed for changes that have made many industries rethink their practices. In entertainment, for example, many companies and shows now avoid using live animals in performances.
What is a PETA Campaign?
- Definition: PETA campaigns are targeted actions that raise awareness or challenge specific practices involving animals. They are known for their bold, sometimes controversial tactics, which aim to draw maximum attention.
- Types of Campaigns: PETA’s campaigns span various areas, including factory farming, animal testing, fur and leather production, and animal use in entertainment. Campaign methods range from protests and demonstrations to celebrity partnerships and viral media.
Explain PETA and Fashion
- PETA’s Role in the Fashion Industry: PETA has played a significant role in pushing the fashion industry toward ethical practices. The organization advocates for cruelty-free alternatives and is a major voice against the use of animal products like fur, leather, wool, and exotic skins.
- Fashion Initiatives: PETA campaigns encourage the use of synthetic and plant-based materials as alternatives to animal-derived products. They’ve influenced brands and designers worldwide to adopt cruelty-free collections, support vegan leather, and avoid harmful practices toward animals.
- Educational Programs: PETA educates consumers on the impacts of traditional fashion materials on animals and promotes the benefits of choosing cruelty-free products. This approach has sparked trends like “vegan fashion” and increased demand for ethical options in mainstream markets.
Conclusion
PETA’s anti-fur campaign has undoubtedly had a profound effect on global attitudes toward fur, particularly in Western countries where animal rights and ethical consumerism have gained traction. Through bold campaigns, celebrity endorsements, and strategic media efforts, PETA succeeded in challenging the fashion industry’s reliance on real fur. However, the campaign’s universality was hindered by cultural, economic, and regional differences. While it was widely embraced in some areas, it faced resistance in places where fur is still seen as a traditional, economic, or luxury product.
Ultimately, PETA’s anti-fur campaign has been influential, if not universal. It has altered the landscape of the fashion industry, led to legal reforms, and contributed to the rise of alternative materials. However, fur continues to be a symbol of status and necessity in some regions, demonstrating that PETA’s campaign, while impactful, has not been universally successful.
FAQs: Was PETA’s Anti-Fur Campaign Universal?
-
Why did PETA start the anti-fur campaign?
PETA launched the anti-fur campaign to raise awareness about the cruelty involved in fur farming and the killing of animals for fashion. They wanted to educate the public on the inhumane practices of the fur industry and encourage the use of alternatives.
-
Has PETA’s anti-fur campaign been successful?
Yes, the campaign has led to a significant decline in the use of fur in fashion, with several major designers and fashion houses adopting fur-free policies. PETA’s efforts have also contributed to legislative changes in certain countries, banning fur farming and sales.
-
Why do some people still support wearing fur?
Some people continue to support wearing fur due to cultural reasons, economic factors, or simply because of fashion preferences. In some parts of the world, fur is seen as a necessary part of life, especially in colder regions where it provides warmth.
-
What are some alternatives to real fur?
Faux fur, vegan leather, and other synthetic materials have emerged as alternatives to real fur. These options provide the same aesthetic without the ethical concerns related to animal cruelty.
-
How has PETA’s anti-fur campaign affected the fur industry?
PETA’s campaign has had a significant impact on the fur industry, leading to a decline in consumer demand for real fur and encouraging many fashion brands to switch to cruelty-free alternatives. However, the industry still exists, particularly in luxury markets and regions with strong cultural ties to fur.